Avalanche network is an innovative contract platform that aims to improve blockchain technology regarding interoperability, scalability, and usability. It has a native token, AVAX, used for paying fees, securing the network, and staking.
It was developed by Ava Labs and introduced in a whitepaper by a team of researchers led by Emin Gün Sirer in 2018. The platform aims to provide a highly scalable, secure, and decentralized ecosystem for various applications, including finance, IoT, and other industries.
- Avalanche uses a unique consensus protocol called the Avalanche Consensus, a combination of the Nakamoto Consensus (used in Bitcoin) and the Classical Consensus (used in traditional distributed systems).
- The Avalanche Consensus is based on a new family of consensus protocols called "metastable" protocols. These protocols use random subsampling and repeated voting to achieve consensus quickly and with high confidence.
- In the Avalanche network, nodes communicate with each other using a gossip protocol. When a node receives a transaction, it queries a random subset of nodes to check if they have seen it before. If most queried nodes have seen the transaction, the node accepts it and gossips it to other nodes. This process is repeated until the transaction reaches a certain acceptance threshold, which is considered final.
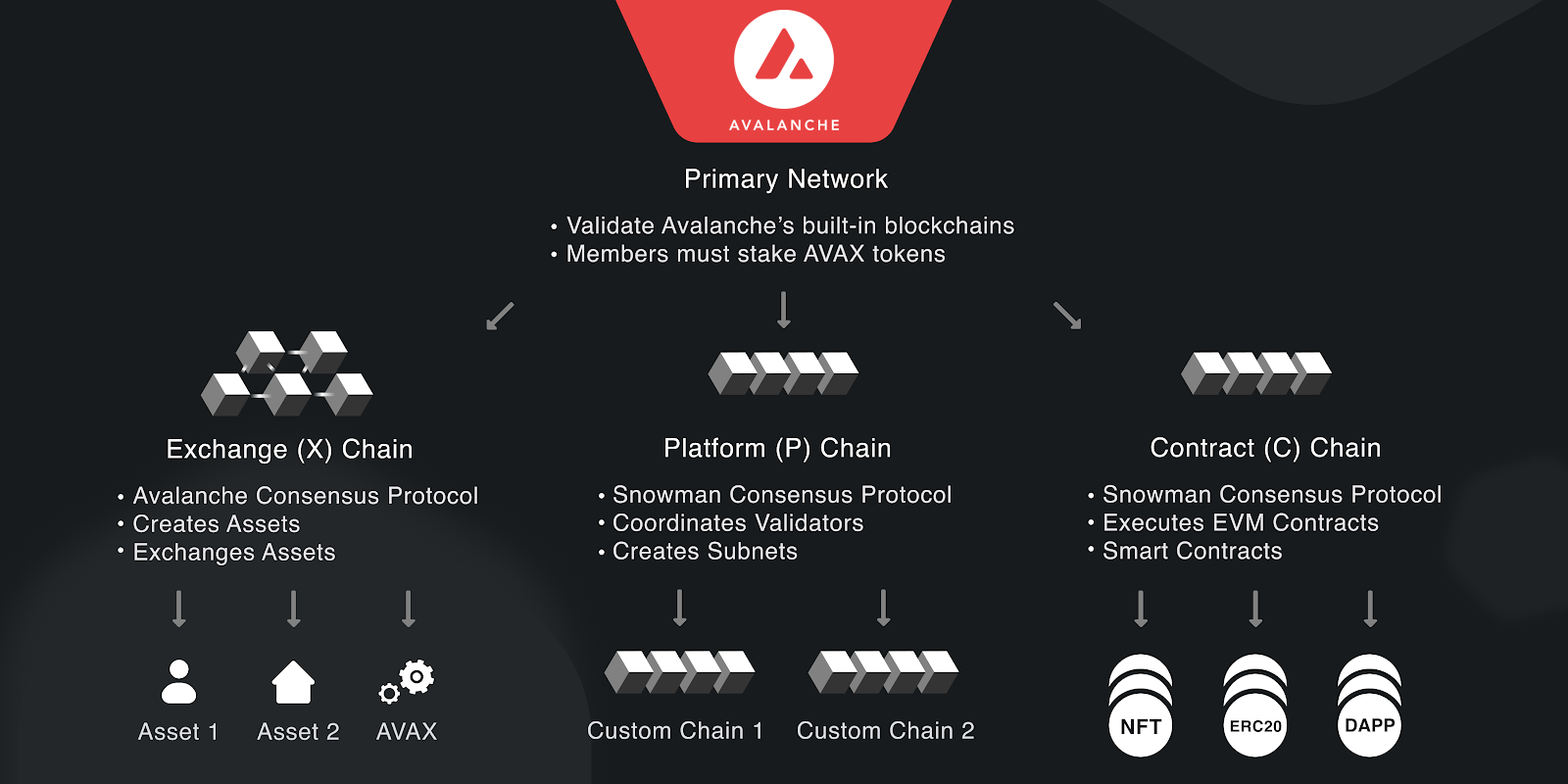
AVAX Architecture
Architecture
Avalanche has unique architecture consisting of three blockchains, each serving a specific purpose. These three blockchains are:
- Platform Chain (P-Chain): The P-Chain is responsible for coordinating validators, managing the Avalanche network's overall security, and maintaining the network's proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanism. Validators stake their AVAX tokens on the P-Chain to participate in the consensus process and earn rewards. The P-Chain also manages creating and maintaining subnets (sub-networks) within the Avalanche ecosystem.
- Exchange Chain (X-Chain): The X-Chain is designed for handling asset creation, trading, and management. It allows users to create and trade digital assets, including custom tokens, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and wrapped versions of assets from other blockchains. The X-Chain uses the Avalanche Consensus to achieve fast transaction finality and high throughput, making it suitable for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and other asset-related use cases.
- Contract Chain (C-Chain): The C-Chain is an Ethereum-compatible smart contract platform that enables developers to deploy and execute smart contracts using the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and Solidity programming language. This compatibility allows developers to easily port existing Ethereum dApps to the Avalanche network and take advantage of its faster transaction finality and higher scalability.
The reason for having three separate blockchains is to optimize each chain for its specific use case, allowing the Avalanche network to achieve high performance and maintain a modular architecture. By separating the responsibilities of the platform, asset exchange, and smart contract execution, Avalanche can ensure that each chain operates efficiently and securely without negatively impacting the performance of the other chains.
This architecture also allows for greater flexibility and customization, as developers can create and deploy their own subnets with specific virtual machines and rule sets tailored to their applications' requirements. This way, Avalanche aims to provide a highly scalable, secure, and customizable platform for a wide range of decentralized applications and use cases.
Which chain shall I use for transferring my AVAX Token?
It depends on your use case. For example, if you want to stake your AVAX tokens, you must transfer them from the X-Chain to the P-Chain. If you use your AVAX tokens in a dApp, you need to transfer them from the X-Chain to the C-Chain.
Do fees differ within the chains?
Yes, the fees differ for each chain on the Avalanche network.
- The fees vary depending on the type of transaction and the chain. For example, creating a new asset on the X-Chain costs 0.01 AVAX, while sending AVAX on the C-Chain costs at least 0.001575 AVAX.
- The fee structure for the Avalanche platform is entirely controlled by user governance, meaning AVAX holders can vote to adjust the fees.
Why use Avalanche?
- Scalability: Avalanche can process thousands of transactions per second, making it suitable for large-scale applications.
- Decentralization: Avalanche can process thousands of transactions per second, making it suitable for large-scale applications.
- Fast finality: Transactions on the Avalanche network achieve finality in seconds, compared to minutes or hours in other blockchains.
- Energy efficiency: Avalanche uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanism, which is more energy-efficient than the proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism used in Bitcoin.
- Reward structure incentivizes participation: Validators on the Avalanche network can earn AVAX rewards by staking their tokens and providing security and performance to the network. The reward rate is determined by governance voting.
- Capable of supporting many blockchain-based projects: Avalanche network can host a variety of projects, such as decentralized exchanges, DeFi platforms, NFTs, and more. It also enables interoperability between different blockchains through bridges and subnets.

Networks
What are Subnets?
Imagine that Avalanche Network is a big city with many buildings. Each building represents a blockchain that can do different things, like sending money, creating art, or playing games. The people living in the buildings are the validators who ensure the blockchains work properly and follow the rules. They use AVAX tokens to pay for their rent and utilities.
Now, some people (validators) may want to create their own buildings (blockchain) with their own rules and features (different consensus mechanisms, fee structures, etc.). For example, they may want a building that only allows certain people to enter, a building with a unique elevator system, or a building that uses solar power. These people can form a subnet, like a neighborhood of buildings with some common characteristics. They can invite others to join their subnet and live in their buildings. They can also visit other subnets and use their buildings if they follow their rules.
Subnets are helpful because they let people customize their blockchains and make them more efficient and compatible with each other. They also make the city more diverse and dynamic, as new subnets can be created and removed according to the needs and preferences of the people.
Comparison with Leading Blockchains
| Feature | Avalanche | Ethereum | Bitcoin | Binance Smart Chain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consensus mechanism | Avalanche consensus | Proof-of-Stake | Proof-of-Work | Proof-of-authority |
| Transaction speed | Sub-second finality | ~15 seconds (average) | ~10 minutes (average) | ~3 seconds (average) |
| Transaction cost | Low (~$0.01) | High (~$15) | Moderate (~$2) | Low (~$0.01) |
| Scalability | High (over 4,500 tps) | Low (15 tps) | Low (7 tps) | High (300 tps) |
| Interoperability | High (supports bridges and subnets) | Moderate (supports layer-2 solutions) | Low (no native support) | Moderate (supports bridges) |
| Ecosystem diversity | High (supports dApps, NFTs, DeFi and more) | High (supports dApps, NFTs, DeFi and more) | Low (mostly used as digital gold) | High (supports dApps, NFTs, DeFi and more) |
Disadvantages
- Still hackable: Some individual projects developed on the Avalanche network have suffered attacks, such as the Zabu Finance platform that lost $3.2 million in an exploit.
- Competition from other platforms: Avalanche network faces competition from other smart contract platforms, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Solana, etc. These platforms may have more users, developers, liquidity, and innovation than the Avalanche network.
In conclusion, Avalanche is a promising blockchain platform with unique features like the Avalanche Consensus, high scalability, and fast transaction finality. It can compete with leading blockchains like Ethereum, Cardano, Solana, and Polkadot. However, as a relatively new platform, it faces challenges in terms of adoption, ecosystem development, and proving its long-term security and stability. As the blockchain space continues to evolve, it remains to be seen how Avalanche will fare against its competitors and whether it can establish itself as a leading platform for decentralized applications.
Thank you for taking the time to read my article.
References:

